Electronics manufactures take part in building a 'smarter world'
Smart phones, smart home devices, smart watches, etc. are becoming infused into the fabric of life. Electronics manufacturing produces a large number of assembled PCB - needed at an affordable price - to be incorporated in equipment like appliances, buildings, vehicles, and industrial controls.
Minimizing human intervention in product setup and changing-over on high-speed SMT assembly lines is critical, to drive out errors, delays, and unproductive time when machines are stopped. In Europe, where manufacturers typically build a high mix of products for industrial, communication, medical, and advanced automotive applications, reducing the workload associated with product changeovers can significantly boost productivity.
Various approaches can be effective. One way is using a combination of production-management software to minimize the setup adjustments needed during product changeover, and additional features built into the equipment itself. This can bring various labor savings, such as eliminating laborious tasks like:
- swapping placement heads
- automating procedures like setting push-up pins
- and innovations to allow routine tasks such as replenishing component reels to be done on the fly without stopping the production line.
Reduce changeover workload boost placement productivity
Using software tools to create production schedules and optimize equipment utilization is essential. Software tools can be especially helpful to enable control over key machines in the line such as screen printer, mounters, and inspection, so these can be consolidated.
The software can give an overview of the overall production requirements and the capabilities of specific lines and individual machines to create feeder configurations that are suited to build multiple different products. Suitable planning can minimize the numbers of changeovers needed on any given shift and hence avoiding production stops and human involvement.
Various packages are available, such as the tools for programming and scheduling, production assistance, and M2M collaboration included in Yamaha’s YSUP intelligent factory software.
However, manufacturers need additional tools at their disposal if they are to successfully minimize machine stoppages to continue raising productivity.
Any time a new setup requires a mounter to be fitted to handle special components (with a different placement head) or feeders need to be changed or simply replenished, the affected machine, and often the entire line, may have to be stopped to allow skilled operators to complete the task.
There are various approaches to solve this issue. Multiple mounters may be installed inline, each setup optimally to place specific types of parts; a chip shooter dedicated to placing small, frequently used parts such as SMD passives can be installed next to a flexible mounter setup to handle a wider range of components.
This may not be ideal, calling for extra investment in equipment and extra space in the factory.
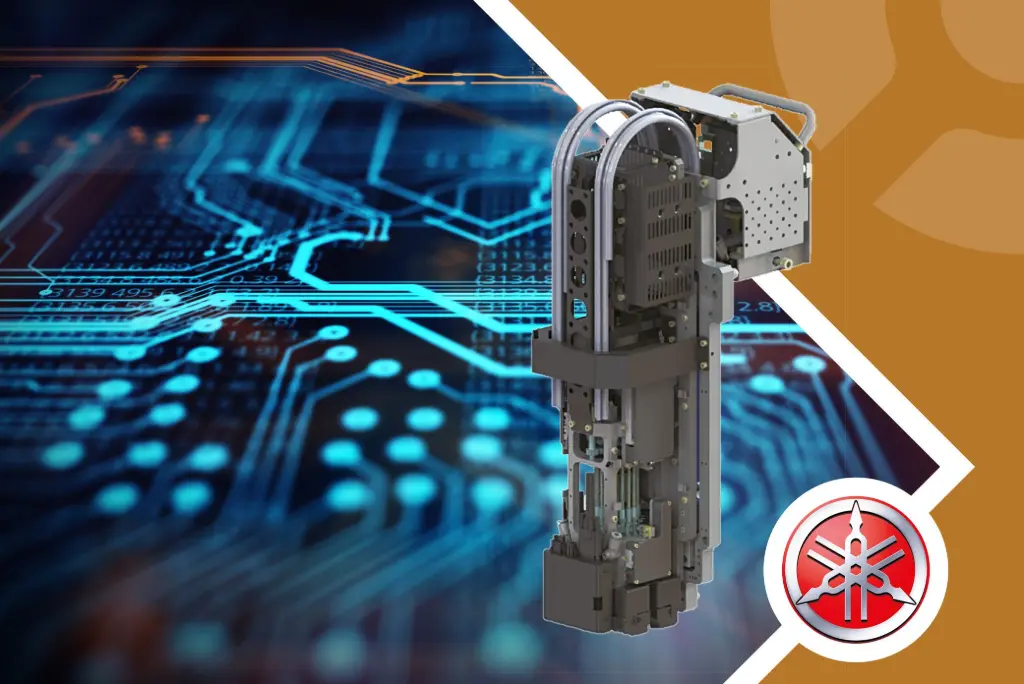 Figure 1. The high-speed rotary RM head extends the one-head concept to provide high-speed placement for a wide component range.
Figure 1. The high-speed rotary RM head extends the one-head concept to provide high-speed placement for a wide component range.Where money and square meters are precious, manufacturers can benefit by using a single, flexible mounter to handle all placement requirements. Yamaha developed the YRM20 next-generation mounter with new features that extend flexibility and automate processes that traditionally have involved time-consuming manual intervention.
This mounter utilizes Yamaha’s one-head solution concept, which now enables even greater productivity with the high-speed rotary RM head (figure 1). This head operates at 115.000 CPH and can place components from 0201 mm SMD chips to parts up to 12 mm x 12 mm and 6.5 mm high.
This allows placement of components such as:
- large LEDs and popular IC styles including chip-scale package (CSP)
- quad flat package (QFP)
- and thin small-outline package (TSOP) at extremely high speed.
There are also new feeders that are optimized to work with the RM head, which deliver parts at high speed and ensure accurate pickup.
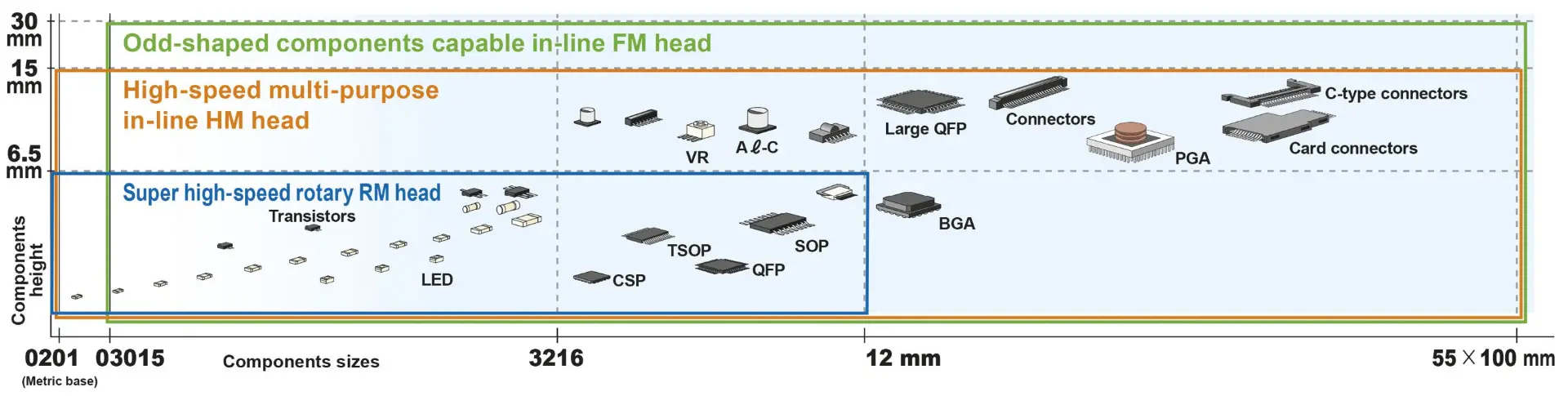
In addition, Yamaha’s universal HM head extends the range of components to include larger parts like electrolytic capacitors, ball-grid array (BGA) ICs, and various types of connectors.
A third option, the ultra-flexible FM head, caters for an even wider range including odd-shaped components and parts up to 55 mm x 100 mm x 30 mm tall. Figure 2 illustrates the typical component types each head can handle.
The Yamaha YRM20 mounter is available in a choice of single-beam dual-beam configurations, giving users flexibility to operate two heads at the same time. To maximize the throughput possible with a two-head setup, Yamaha has incorporated the overdrive motion technology This raises productivity by ensuring the 2 heads can work together with minimal interference (figure 3).
The YRM20’s dual-stage conveyor enhances PCB support and handles panels up to 510 mm wide at high speed to significantly reduce changeover time.
 Figure 3. Yamaha’s overdrive motion ensures that two placement heads can operate independently and interact efficiently.
Figure 3. Yamaha’s overdrive motion ensures that two placement heads can operate independently and interact efficiently.Automating changeovers saves time & eliminate errors
Automating various aspects of the product changeover sequence is also effective in reducing human intervention, and that will save time and eliminate errors.
Auto program changeover eliminate operators task of seeking out the correct new production program to load.
Instead the correct placement machine program is retrieves by scanning the barcode of the next board to be produced. When used with a powered tooling array, linking auto program changeover and automatic push-up pin exchange that raises the required pins to support the PCB during component placement, eliminates another, laborious manual task from the changeover sequence.
In addition, auto-loading feeders are available. These let operators quickly change component reels as they become emptied, ensuring the new carrier tape is correctly inserted without needing to stop the machine. Using Yamaha’s ALF auto-loading feeders, a new tape can be inserted on the fly in as little as five seconds.
With the YRM20, Yamaha has now extended this non-stop changeover concept to handle parts typically presented in trays, such as the largest ICs and connectors. The eATS30 non-stop tray feeder supplies these components continuously and introduces from a streamlined refilling procedure. A single pallet of tray components, or a complete magazine containing 10 pallets, can be inserted without stopping the machine thereby significantly increasing productivity.
Conclusion How to boost placement productivity
By reducing laborious equipment-setup adjustments, such as changing placement heads, and extending non-stop component replenishment to include tray components as well as reels, human intervention in the routine activities can be greatly reduced. Benefits include fewer errors and greater equipment uptime, both contributing to increased productivity.
Relieving experienced operators of these mundane tasks allows them to focus on roles that are critically reliant on human skills and judgement, such as quickly diagnosing – and curing - the causes of any unexpected stoppages that may occur at any time. Additional tools are available to help with this, such as Yamaha’s QA Option software, bringing the benefits of human experience and advanced automation together in pursuit of the ultimate goal: continuously increasing productivity.
How to boost placement productivity